Machine learning (ML) often sounds mysterious to newcomers. You might have heard about “training models” or “teaching machines,” but what does that really mean? And why do experts keep talking about supervised and unsupervised learning?
If you’ve ever wondered how Netflix recommends movies, or how Google Photos groups similar faces automatically this guide will make it crystal clear. At Wamid Academy, we’ll break down these two foundational types of machine learning in plain, beginner-friendly terms, and show you how they work in the real world.
🧭 Table of Contents
- Understanding the Essence of Machine Learning
- What Is Supervised Learning?
- What Is Unsupervised Learning?
- Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning: Main Differences
- How to Choose the Right Type for Your Project
- Where to Start Learning Machine Learning
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Input (features)
- Correct output (label)
- Define your goal: Are you predicting or exploring?
- Check your data: Do you have labeled outcomes?
- Evaluate complexity: Some tasks may start unsupervised (exploration) and then move to supervised (prediction).
- Experiment: Tools like Google Colab or Jupyter Notebook make it easy to test both methods.
- Learn Python basics: It’s the most common ML language.
- Master key libraries: Start with
scikit-learn,pandas, andmatplotlib. - Take small projects: Predict house prices or cluster shopping habits.
- Explore further: Deep learning, natural language processing, or AI ethics.
Understanding the Essence of Machine Learning
Machine learning is the science of enabling computers to learn patterns from data without being explicitly programmed. Think of it like teaching a child: instead of writing every rule by hand, you show examples, and the system learns from them.
At Wamid Academy, we emphasize practical, beginner-friendly projects so you can see how algorithms learn rather than just reading theory.

What Is Supervised Learning?
Supervised learning happens when we teach a model using labeled data meaning each training example already includes the correct answer. In other words, the algorithm knows what it should learn to predict.
You provide:
Then the model learns to map inputs to outputs accurately.
Real Life Example Email Spam Detection
Imagine your email inbox. Each message can be either spam or not spam. We train the model by feeding it hundreds (or millions) of labeled examples:
| Email Text | Label |
|---|---|
| “You’ve won a million dollars!” | Spam |
| “Your Amazon order has shipped” | Not Spam |
After training, when a new email arrives, the model can automatically predict whether it’s spam or not.
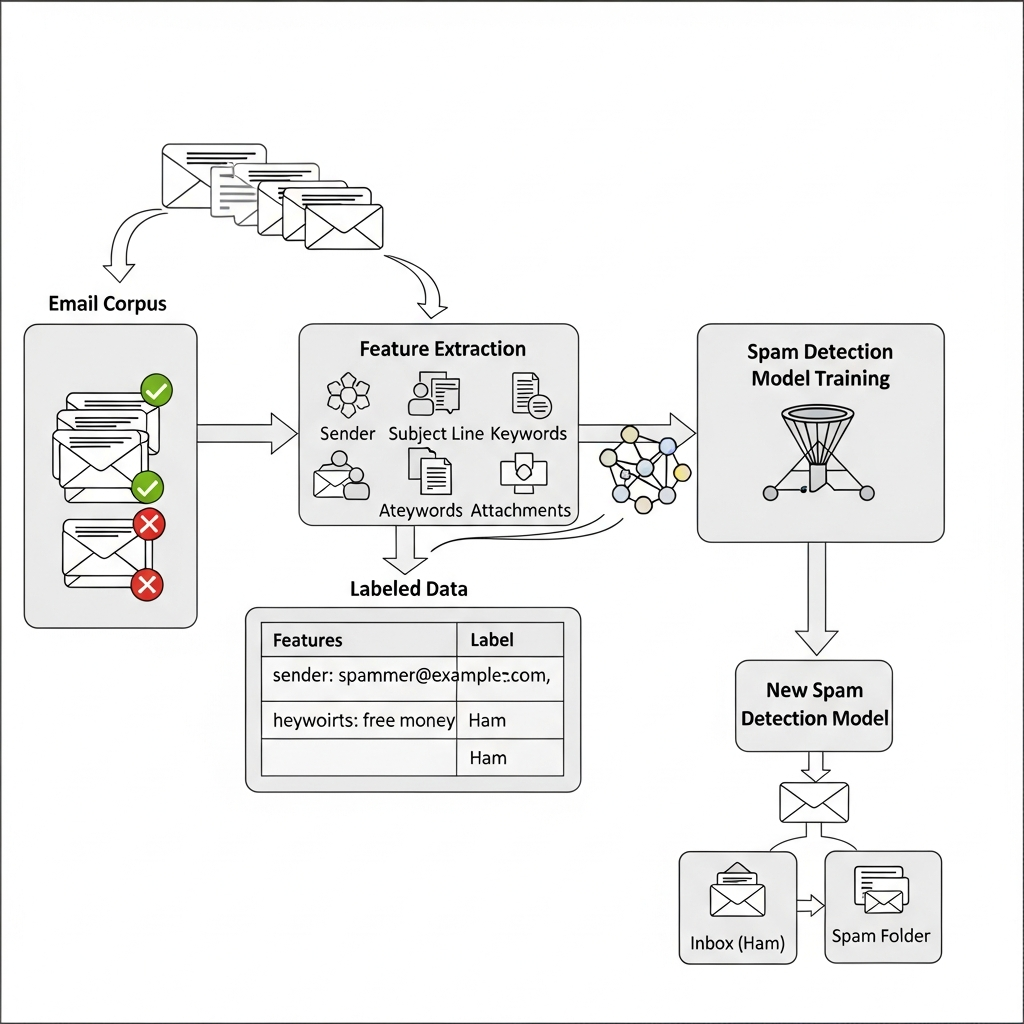
Key Algorithms Used in Supervised Learning
| Algorithm | Type | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | Regression | Predicting housing prices |
| Logistic Regression | Classification | Email spam filtering |
| Decision Trees | Both | Credit scoring |
| Random Forests | Both | Sales forecasting |
| Support Vector Machines (SVM) | Both | Face recognition |
What Is Unsupervised Learning?
Unsupervised learning is when the model is given unlabeled data it has no idea what the correct output is. The goal? To discover hidden structures, patterns, or relationships within the data. This is like giving a child a box of mixed toys and asking them to group them however they think makes sense.
Real-Life Example: Customer Segmentation
A marketing team has thousands of customers, but no idea how to target them effectively.
By applying unsupervised learning, they can automatically group customers based on buying habits, age, or income without knowing the “correct” groupings beforehand.
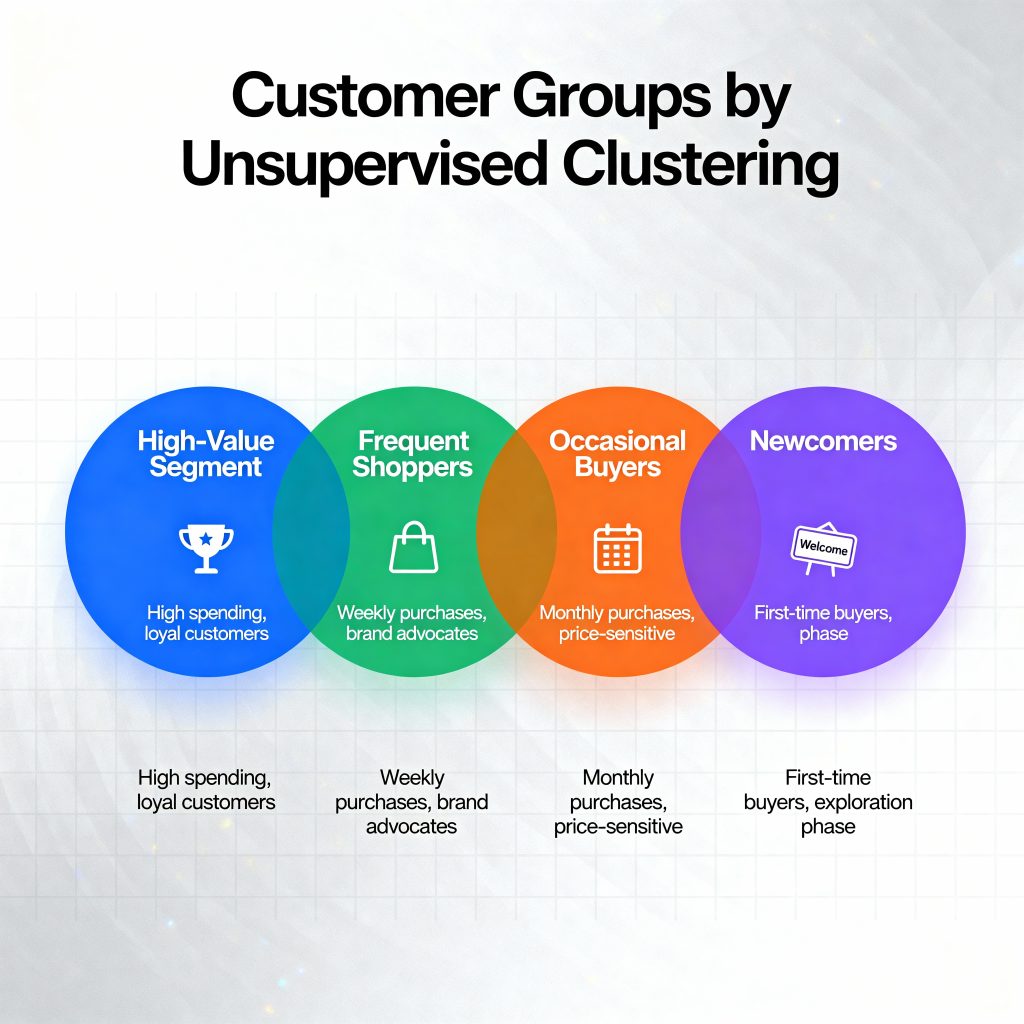
Key Algorithms Used in Unsupervised Learning
| Algorithm | Purpose | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| K-Means Clustering | Grouping | Customer segmentation |
| Hierarchical Clustering | Grouping | DNA sequence analysis |
| Principal Component Analysis (PCA) | Dimensionality reduction | Image compression |
| Autoencoders | Pattern detection | Anomaly detection |
Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning: Main Differences
| Feature | Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Labeled | Unlabeled |
| Goal | Predict outcomes | Discover structure |
| Output | Specific predictions | Clusters or patterns |
| Example | Predict exam scores | Group students by learning style |
| Difficulty | Easier to evaluate | Harder to interpret |
Quick Tip: If you already have known outcomes (like spam vs not spam), use supervised learning.
If not, and you just want to find patterns (like grouping customers), use unsupervised learning.
How to Choose the Right Type for Your Project
At Wamid Academy, our beginner-friendly Machine Learning Fundamentals course guides you through both approaches step-by-step with real-world datasets.
Where to Start Learning Machine Learning
🔗 Check out Wamid Academy’s guide: [How Long Does It Take to Learn Machine Learning?]
🌍 External Source: Scikit-learn Official Documentation
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Do I need math skills to start machine learning?
You need basic algebra and probability, but many beginner tools make it visual and intuitive.
Q2: Is supervised learning easier for beginners?
Yes. Since the outcomes are labeled, it’s easier to measure how well your model performs.
Q3: Can I use both methods in one project?
Absolutely! Many real-world systems combine both for example, clustering customers first, then predicting their future purchases.
Q4: Which one is used in AI applications like ChatGPT?
Mostly supervised learning (fine-tuning) combined with other advanced methods like reinforcement learning.
Start Your ML Journey Today
Machine learning isn’t as intimidating as it seems. Once you understand the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning, you’ve mastered the first major concept.
At Wamid Academy, we make learning practical and enjoyable helping you go from beginner to confident practitioner step by step.
Ready to begin? Explore our beginner-friendly ML courses and start building your first model today!
