Smart Contract vs dApp: Key Differences Explained
Navigating the world of blockchain technology can feel overwhelming, especially for newcomers seeking to build decentralized applications. The landscape is rich with jargon and complex concepts, making it difficult to distinguish between similar terms. One common confusion involves smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), which are integral to the web3 ecosystem. Understanding the critical differences between these two components is essential for anyone looking to engage in blockchain development. This comprehensive guide will clarify their distinctions, explore real-world applications, and provide actionable steps for those eager to dive deeper into the blockchain realm.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Smart Contracts
- What Are dApps?
- Key Differences Between Smart Contracts and dApps
- Real-World Examples
- Getting Started with Smart Contracts and dApps
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Understanding Smart Contracts
Definition of Smart Contracts
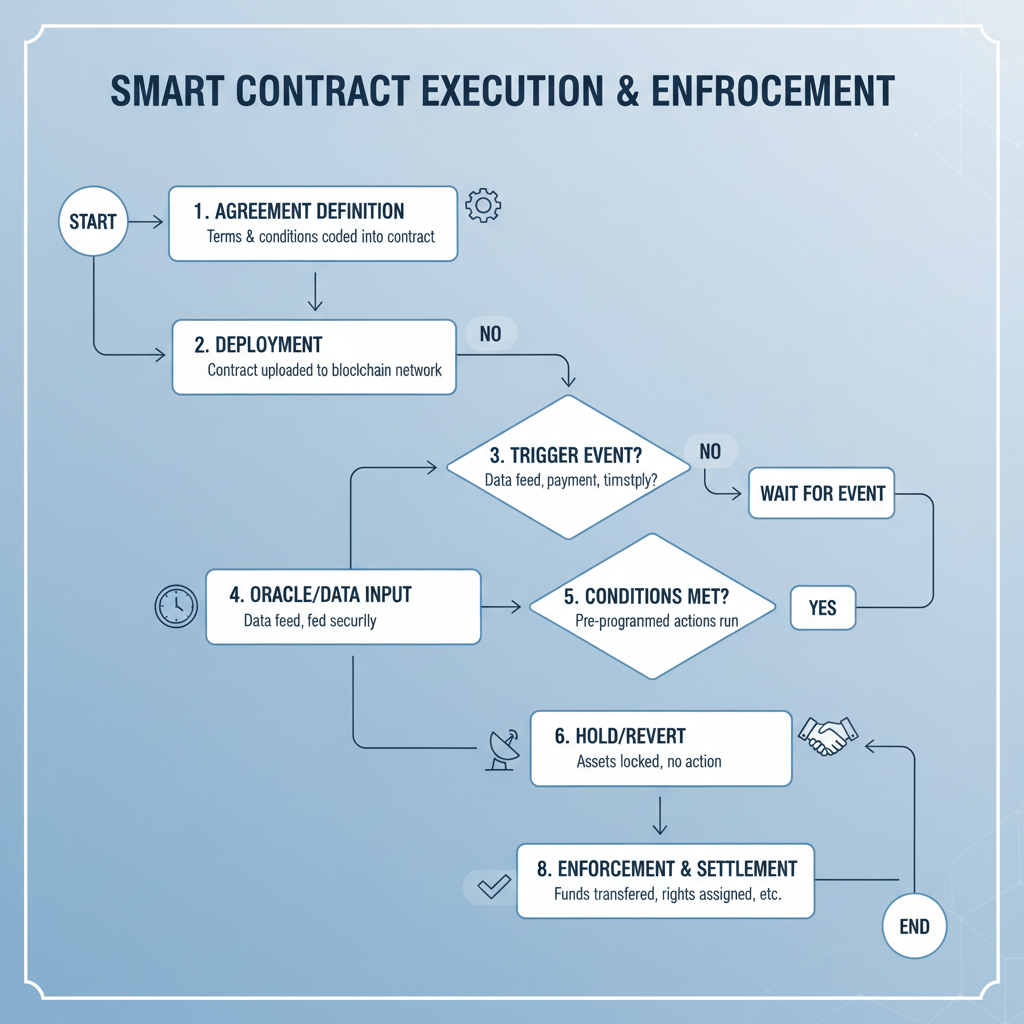
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They run on blockchain networks, and the execution of the contract is enforced by the network itself, ensuring a trustless environment where parties can transact without intermediaries.
How Smart Contracts Work
Smart contracts utilize blockchain technology for secure transactions. Once deployed on the blockchain, they facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. For example, a smart contract can automatically release a payment when services are fulfilled, eliminating the need for an escrow.
What Are dApps?
Definition of dApps
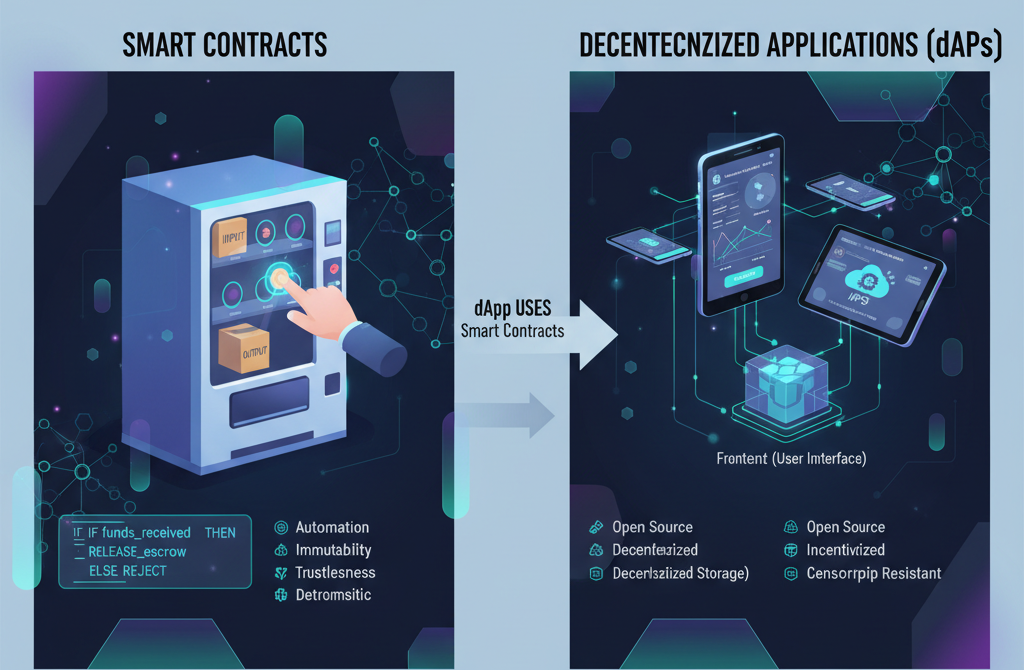
Decentralized applications (dApps) are applications that run on a decentralized network, typically utilizing smart contracts for backend operations. Unlike traditional applications that run on centralized servers, dApps are governed by a blockchain protocol and are resistant to censorship and fraud.
How dApps Function
dApps leverage smart contracts to operate independently. Users interact with the dApp through a user interface, while the underlying logic and data management are handled via smart contracts on the blockchain. This structure allows for transparency and security, enhancing user trust.
Key Differences Between Smart Contracts and dApps
| Feature | Smart Contracts | dApps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-executing contracts on blockchain | Applications that utilize smart contracts |
| Functionality | Executes predefined conditions | Offers complete user interface and interaction |
| Dependency | Standalone contract | Dependent on smart contracts for backend |
| User Interaction | Not directly interacted with by end users | Direct user interaction through interfaces |
| Purpose | To automate and enforce agreements | To deliver services and functionalities |
Real-World Examples
Smart Contract Example
Imagine a real estate transaction where a smart contract automatically transfers the ownership of a property once the payment is verified. This process eliminates the need for a notary or escrow service, mitigating delays and costs associated with traditional real estate deals.
dApp Example
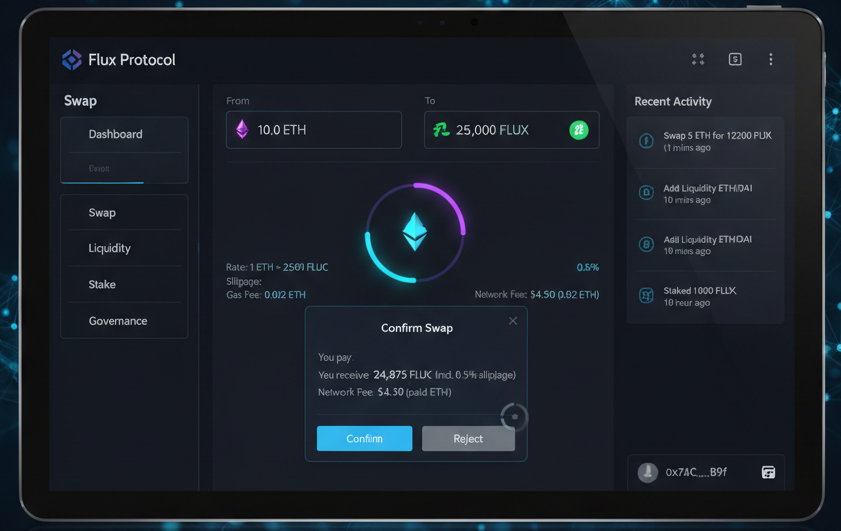
One of the well-known examples of a dApp is Uniswap, a decentralized trading protocol. Users can swap various cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets, with smart contracts ensuring the security and efficiency of trades without the need for a central authority.
Getting Started with Smart Contracts and dApps
Actionable Steps
- Learn the Basics: Start with fundamental blockchain courses at Wamid Academy. Understanding blockchain technology is crucial as it forms the backbone of both smart contracts and dApps.
- Explore Coding Languages: Familiarize yourself with Solidity, the primary language used to write Ethereum smart contracts, and JavaScript for developing dApps.
- Build a Simple Project: Begin with a small project, like a basic smart contract that automates a simple agreement. Then escalate to creating a dApp that utilizes your smart contract.
- Connect with the Community: Join forums and Telegram groups related to blockchain development to share insights, seek advice, and collaborate on projects.
Resources for Learning
- Wamid Academy’s courses on Blockchain Fundamentals and Solidity Programming.
- Online platforms like Ethereum documentation and GitHub for exploring code examples.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the primary purpose of smart contracts?
Smart contracts automate and enforce contracts without the need for intermediaries, providing efficiency and transparency.
Can you use smart contracts without dApps?
Yes, smart contracts can function independently; however, they typically enhance dApps’ capabilities by providing automation and trustless execution.
How does one ensure the security of smart contracts?
Smart contracts must undergo extensive testing and audits to ensure their code is free from vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
Are dApps completely decentralized?
While dApps design aims for decentralization, some may still have central components (e.g., governance) that could affect their distributed nature.
Explore more courses at Wamid Academy to deepen your understanding of blockchain technology and its applications!
